"It's like Google Earth for the body," said IBM Researcher Andre Elisseeff, who leads the healthcare projects at IBM's Zurich lab. "In hopes of speeding the move toward electronic healthcare records, we've tried to make information easily accessible for healthcare providers by combining medical data with visual representation, making it as simple as possible to interact with data that can improve patient care."
 For example, when a patient visits a doctor's office today and complains of back pain, the doctor will ask the patient about any history the patient can recall, do tests, and visually and physically examine the patient. After that, the doctor will usually sort through stacks of paper records but will most likely not have access to the full patient history and similar complaints.
For example, when a patient visits a doctor's office today and complains of back pain, the doctor will ask the patient about any history the patient can recall, do tests, and visually and physically examine the patient. After that, the doctor will usually sort through stacks of paper records but will most likely not have access to the full patient history and similar complaints.
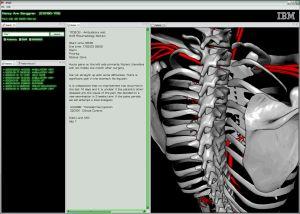
The ASME system will allow doctors to "click" on different parts of the 3-D avatar of the human body - for example, the spine - and instantly see all the available medical history and information related to that patient's spine, including text entries, lab results and medical images such as radiographs or MRIs. Or the doctor might be interested only in information related to a particular part of the spine; in this case, the practitioner can zoom in, narrowing the search parameters by time or other factors.
Using advanced machine learning and state-of-the-art 3D modeling techniques, the IBM researchers overcame key technical challenges including integrating heterogeneous data sources and complex text-based information -- so-called unstructured data -- and linking that data to the anatomical model in a meaningful and easy-to-navigate way. ASME also uses SNOMED, the systemized nomenclature of medicine that encompasses approximately 300,000 medical terms, to create a bridge between graphical concepts and text documents.
ASME is the result of a collaboration between IBM Denmark and IBM Research. By bringing its sales force and its research organization together, IBM has created a unique innovation team with deep understanding of the industry and leading technical expertise.
The need for Electronic Health Records
Advances in technology are driving great breakthroughs in medical treatment and care, but today's health records do not fully take advantage of what is available. Patient records are static and flat-consisting either of unstructured data written on paper or more structured text information stored in various databases. In either case, the records provide disparate bits and pieces of information on diagnoses and diseases; accessing a comprehensive history proves to be an enormous challenge.
Because the industry is still in the very early stages of achieving a fully functional electronic health records (eHR) system, which would enable the sharing of information among hospitals, clinics and other providers in a way that protects individual patient privacy, most medical professionals prefer to use paper records or their own proprietary system for keeping eHRs. But what if a system could bring together all these flat and static pieces to derive a dynamic and full picture of a patient's health status in real-time? And what if the system were to provide this information in an intuitive and easy-to-use way? With ASME, IBM researchers have now presented such a system -- ASME allows navigating through a virtual map of the human body, an intuitive approach for healthcare professionals.
Building on previous IBM healthcare IT milestones, ASME is the medical information hub that semantically integrates information from IBM's Health Information Exchange (HIE) with a virtual model of the human body.
Moving forward, the researchers will explore integrating speech technology into ASME.
Related news articles:
- IBM Healthcare's Profile
For more information about IBM, please visit www.ibm.com.