Intelligent biomedical clothes are a key element in the prevention and early detection of diseases. Smart fabrics with embedded sensors can monitor different aspects of the human body. Clothes made of such fabrics provide user-friendly ways of monitoring patients over extensive periods of time, thus reducing the need for doctors' appointments and hospital visits. The data collected by the wearable sensors is transmitted electronically to telemedicine centres via fixed or wireless communication networks. When the data indicates a need for concern, alarms or warnings are generated by the electronic systems. The process saves time and increases patient-doctor interaction. Intelligent biomedical clothes could benefit a wide range of people:
- People who just want to stay fit and healthy;
- Healthy people who know they are at risk of developing specific illnesses but want to remain healthy;
- Chronically ill patients by helping them manage their condition effectively; and
- Vulnerable people, such as the elderly, by enabling them to live as independently as possible, for as long as possible, outside traditional care institutions.
The European Commission has supported the development of intelligent biomedical clothes throughout the Fifth and Sixth Framework Programmes. For instance, under FP6, â¬64 million was devoted to textiles projects, 30% of which was targeted at clothing. A number of prototype systems, such as the garments developed in the WEALTHY and MYHEART projects are a direct result of this spending. The forthcoming Seventh Framework Programme provides for more support for research in this field in order to further develop the potential of intelligent fabrics. A couple of examples of this are the "Application of New Materials including Bio-based Fibres in High-Added Value Textile Products" objective, which is being developed under the NMP Programme (on Nanosciences, Nanotechnologies, Materials and New Production Technologies) and the "Personal Health Systems for Monitoring and Point-of-Care diagnostics" project, which comes under the umbrella of the Information and Communication Technology Programme.
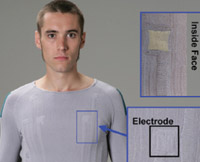 Lucy, a 29 year-old engineer, runs regularly, eats sensibly and generally takes care of herself. For the past month, Lucy has been experiencing heart palpitations so she goes to her GP for a complete check up. Despite her youth and healthy lifestyle, Lucy's test results indicate that she is at relatively high risk of having a heart attack. Lucy is keen to maintain her lifestyle so she has a discussion with her doctor about how best to manage her health problem. Her doctor is as keen as Lucy is that her heart should continue to benefit from regular sport so he suggests that she wears intelligent clothing to monitor her heart while she runs.
Lucy, a 29 year-old engineer, runs regularly, eats sensibly and generally takes care of herself. For the past month, Lucy has been experiencing heart palpitations so she goes to her GP for a complete check up. Despite her youth and healthy lifestyle, Lucy's test results indicate that she is at relatively high risk of having a heart attack. Lucy is keen to maintain her lifestyle so she has a discussion with her doctor about how best to manage her health problem. Her doctor is as keen as Lucy is that her heart should continue to benefit from regular sport so he suggests that she wears intelligent clothing to monitor her heart while she runs.
Tiny sensors integrated into her clothing monitor Lucy's heart rate and send out a signal if she needs to slow down. This simple device enables Lucy to continue to run, safe in the knowledge that she is not putting herself at risk. The world of fashion is set to be taken by storm by intelligent clothing that works as you wear!
Examples of FP6 research projects on intelligent clothing:
- FLEXIFUNBAR addresses research issues on emerging technologies for the production of new flexible structures (paper, leather and technical textiles for applications in transport, medicine, security and clothing). The project's various activities simultaneously focus on integrated areas of research and scaling up (nanostructures, materials research for barrier effects, new production processes);
- DIGITEX has the clear strategic objective of achieving a completely new industrial process for the coating of textiles based on digital printing technologies, and in particular textiles for safety performance and industrial workwear in services and industry. The technology used involves the Integration of nanoparticles in fluids to be jetted onto textiles (Digital jetting technique) giving rise to anti-flame, anti-chemical, and bacteria-proof functionalities;
- INTELTEX is expected to have a high potential impact for the smart textile sector by developing novel, sensitive and functional Conductive Polymer Composite-based textiles for construction, medical and protective clothing applications. They could be used in medical wear for monitoring body temperature and protective clothing such as that used by firemen;
- LEAPFROG aims at the modernisation and ultimate transformation of the entire textile industry. It is the outcome of a long process conducted by EURATEX, the European Apparel and Textile Organisation. The project addresses virtual prototyping where advanced simulation tools enable designers to virtually prototype a garment collection in terms of style, size and functionality;
- MYHEART develops intelligent systems for the prevention and monitoring of cardiovascular diseases. The project develops smart electronic and textile systems and appropriate services that empower the users to take control of their own health status.
Source: Europe Direct Newsletter
For further information, please visit:
- FLEXIFUNBAR - the objective of Flexifunbar is to develop and promote multi-functional flexible structure for use in many multisectorial industrial applications in the health field as well as in the building construction and transportation industrie...
- DIGITEX - a joint research and innovation initiative of the European textile and clothing industry born to a Consortium Agreement made of the best companies working in textile and clothing industry and research centres which will attempt to develop and implement new ways of optimal fabric preparation for clothing production...
- MYHEART - the MyHeart mission is to empower citizen to fight cardio-vascular diseases by preventive lifestyle and early diagnosis...